Packaging design for food products plays a crucial role in attracting customers and ensuring product success in the competitive retail environment. Effective food packaging not only protects the contents but also communicates brand identity, product information, and appeal to consumers. As the first point of contact between a product and potential buyers, packaging has a significant influence on purchasing decisions.
This guide offers a comprehensive approach to mastering food packaging design. It covers understanding target markets, developing brand identity, crafting effective package designs, and testing and refining concepts. By following these steps, food packaging designers and brands can create packaging that stands out on shelves, aligns with current trends, and resonates with consumers. The guide also explores eco-friendly packaging options and innovative ideas to enhance product visibility and appeal.
Understanding Your Target Market
To create effective packaging design for food products, it is crucial to have a deep understanding of the target market. This involves conducting thorough market research, creating buyer personas, and analysing competitor packaging.
Conducting Market Research
Market research plays a vital role in developing successful packaging design for food products. It helps companies establish what their customers want, how feasible it would be to deliver, and what their competitors are doing. By conducting extensive market research, businesses can gain valuable insights into consumer preferences, trends, and purchasing behaviours.
One effective way to gather information is through surveys, focus groups, and online interactions. These methods allow companies to talk directly to their customers and understand their pain points and desires. For instance, if research reveals that customers are particularly concerned about the environment, it may be wise to focus on eco-friendly packaging and promote this aspect in marketing efforts.
Market research can also uncover opportunities for upselling existing products or even inspire ideas for entirely new products. By identifying trends and learning about what the specific customer base is passionate about, companies can create packaging that satisfies consumer demands and signals that they are the kind of company customers want to support.

Creating Buyer Personas
Buyer personas are semi-fictitious representations of a target audience that summarise the characteristics of a population segment in a single description. These personas help businesses focus on something tangible rather than abstract data, making it easier to understand which content, methods, and tools to use to connect with the customer base.
When creating buyer personas for packaging design for food products, it’s important to consider both demographics and psychographics. Demographics include factors such as age, gender, income level, and education level, while psychographics encompass lifestyle choices and hobbies.
For example, a buyer persona might be Jennifer, a single millennial mum with two young school-age children who works full-time as a paralegal in Chicago. From this information, we can deduce that she is active on social media, has a middle income, and is busy. She likely values convenience, price, and healthful items due to pressure from social media messaging to be a good mum.
By defining clear buyer personas, businesses can tailor their packaging design for food products to meet the specific needs and preferences of their target audience. This approach can lead to increased sales and improved user satisfaction and experience.
Analysing Competitor Packaging
Examining competitor packaging is an essential step in creating effective packaging design for food products. While it’s not about copying designs, it’s important to understand how a product’s packaging will fit within the context of its shelf neighbours.
When analysing competitor packaging, consider factors such as colour contrast, shape, and functionality. If competitors use warm colour palettes, a cool blue or green package design might help a product stand out on the shelf. Similarly, if the market leaders in a category share certain design elements, incorporating those elements can help position a product as a major player in that space.
It’s also crucial to assess the functionality and convenience of competitors’ packaging. Does it allow for reuse of the product? If it does any of these things poorly (or not at all), there may be an opportunity to improve upon it.
By conducting thorough market research, creating detailed buyer personas, and analysing competitor packaging, businesses can develop packaging design for food products that resonates with their target audience and stands out in the retail environment.
Developing Your Brand Identity
Developing a strong brand identity is crucial for creating effective packaging design for food products. It involves defining brand values, creating a unique visual style, and designing a logo that resonates with the target audience. These elements work together to establish a cohesive brand identity that stands out in the competitive retail environment.
Defining Your Brand Values
Brand values are the core principles that guide a company’s actions, behaviours, and decision-making processes. They reflect what the brand stands for and what it believes in. For food brands, these values might include concepts such as quality, sustainability, innovation, or customer focus.
To define brand values, companies can use various techniques. One approach is to create a mood board with images that reflect the desired brand identity. This visual representation can help evoke emotions and convey intangible concepts like culture and ethos at a non-verbal level.
Another method is to define an archetype for the brand. This could be an abstract character, such as a hero, explorer, or caregiver, or even a famous person. The chosen archetype indicates specific values and personality traits that the brand wishes to embody.
It’s also important to map the unique space the brand occupies in the market. By analysing competitors’ values and identifying gaps, companies can define values that differentiate their brand and make it appealing to consumers.
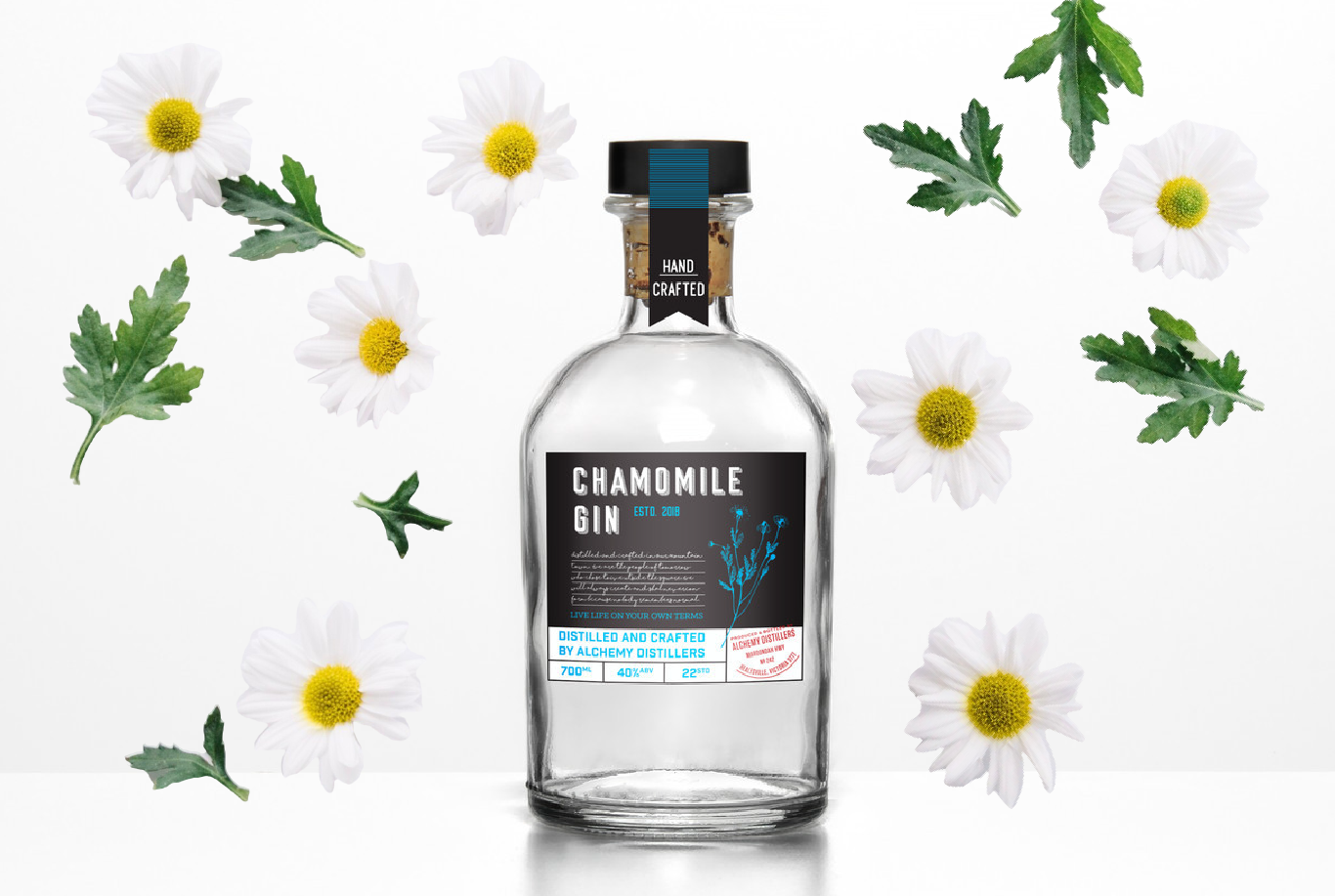

Creating a Unique Visual Style
Once brand values are established, the next step is to create a unique visual style that reflects these values. This involves selecting colours, fonts, and imagery that align with the brand’s identity and appeal to the target audience.
Colour has a significant impact on food packaging design. The chosen colour palette should evoke the desired emotions and align with the overall branding strategy. For example, eco-friendly brands might opt for earthy tones, while luxury food products might use gold or deep, rich colours.
Typography is another crucial element of visual style. The chosen fonts should be legible and consistent with the brand’s personality. They should work well across various packaging sizes and formats while maintaining clarity and impact.
Designing Your Logo
The logo is perhaps the most important visual element of a brand’s identity. For food packaging design, the logo should be simple, versatile, and reflective of the brand’s identity. It should capture the essence of the food brand and be easily recognisable across various platforms, from packaging design to social media.
When designing a logo for food products, it’s important to consider how it will look on different packaging materials and sizes. The logo should be scalable and maintain its impact whether it’s on a small snack packet or a large cereal box.
By carefully developing these elements of brand identity, companies can create packaging design for food products that not only stands out on the shelf but also resonates with consumers and builds long-term brand loyalty.
Crafting an Effective Package Design
Crafting an effective package design for food products involves careful consideration of various elements to create a visually appealing and functional package that stands out in the retail environment. This process includes choosing appropriate packaging materials, creating eye-catching graphics, and incorporating essential information.
Choosing Packaging Materials
Selecting the right packaging materials is crucial for food product packaging design. The choice of materials has an impact on both the product’s preservation and its environmental footprint. Plastic wrap, for instance, is a common and cost-effective option that keeps food fresh. Glass jars offer durability and recyclability, while tin cans provide excellent protection for long-term storage. Cardboard boxes are versatile and can be easily printed with branding messages.
For businesses looking to enhance their sustainability efforts, eco-friendly options are gaining popularity. These include biodegradable materials like corn starch, which can be used to make plates, trays, and portion-sized boxes. Some innovative companies are even exploring the use of mushrooms and waste avocado seeds to create compostable packaging.
When selecting packaging materials, it’s essential to consider factors such as barrier properties, food safety, sustainability, carbon footprint, costs, and ease of use for consumers. The chosen material should align with the brand’s values and resonate with the target audience.
Creating Eye-Catching Graphics
The visual appeal of food packaging design plays a significant role in attracting consumers’ attention. Colour has a powerful influence on consumer psychology and can evoke specific emotions and brand associations. For instance, green often signifies freshness and eco-friendliness, while purple can convey luxury and indulgence.
When designing graphics for food packaging, it’s crucial to consider the product’s nature and target market. The design should harmonise with the overall brand identity and values. Typography also plays a vital role in creating an effective package design. The chosen fonts should be legible and consistent with the brand’s personality, working well across various packaging sizes and formats.
To maximise shelf impact, designers can use colour contrasts to make the product stand out. However, it’s essential to strike a balance between visual attractiveness and practicality. The packaging design should tell a compelling story about the brand’s commitment to quality and overall integrity.
Incorporating Essential Information
Food packaging must include specific information to comply with regulations and inform consumers. This includes the product name, a ‘best before’ or ‘use by’ date, any necessary warnings, net quantity information, and a list of ingredients. The country or place of origin, lot number, special storage conditions, and cooking instructions (if necessary) should also be included.
For products sold in Great Britain, the packaging must display the name and address of the UK or EU business responsible for the information. In Northern Ireland, the name and address of the Northern Irish or EU business must be shown. The net quantity must be clearly visible, usually close to the product name.
By carefully considering these elements – packaging materials, eye-catching graphics, and essential information – designers can create effective packaging design for food products that not only protects the contents but also communicates brand identity and appeals to consumers in the competitive retail environment.
Testing and Refining Your Design
Once a packaging design for food products has been created, it’s crucial to test and refine it to ensure its effectiveness in the retail environment. This process involves gathering feedback from consumers and making necessary adjustments to improve the design’s appeal and functionality.
Conducting Focus Groups
Focus groups are a valuable tool for gaining insights into consumer perceptions of packaging design for food products. These sessions involve gathering a small group of target consumers to discuss their thoughts and feelings about the proposed design. During focus groups, participants can provide feedback on various aspects of the packaging, such as its visual appeal, ease of use, and how well it communicates the product’s benefits.
When conducting focus groups for food packaging design, it’s important to ask specific questions about the design elements, such as colours, typography, and imagery. This feedback can help identify any potential issues or areas for improvement in the design. Additionally, focus groups can provide valuable insights into consumer preferences and behaviours, which can inform future design decisions.
A/B Testing Different Designs
A/B testing is an effective method for comparing two different versions of a packaging design to determine which one performs better. This approach involves creating two variations of the design, typically changing one specific element, such as the colour scheme or typography. Both versions are then presented to consumers to gauge their reactions and preferences.
When conducting A/B testing for food packaging design, it’s important to focus on one variable at a time to accurately measure its impact. For example, a company might test two different colour schemes for their product packaging while keeping all other elements constant. This approach allows for a clear understanding of which design elements resonate most with consumers.
Iterating Based on Feedback
The final step in testing and refining packaging design for food products is to iterate based on the feedback received from focus groups and A/B testing. This process involves making adjustments to the design to address any issues or concerns raised by consumers, as well as incorporating elements that received positive feedback.
Iteration may involve tweaking colours, adjusting typography, or refining imagery to better align with consumer preferences and expectations. It’s important to approach this process with an open mind and be willing to make significant changes if necessary to create a packaging design that truly resonates with the target audience.
By thoroughly testing and refining packaging design for food products, companies can create packaging that not only stands out on the shelf but also effectively communicates the product’s benefits and appeals to consumers in the competitive retail environment.
Conclusion
Mastering packaging design for food products has a significant influence on brand success and consumer engagement. This comprehensive guide provides valuable insights to understand target markets, develop brand identity, craft effective designs, and refine concepts through testing. By following these steps, designers and brands can create packaging that not only protects the product but also communicates brand values and appeals to consumers in the competitive retail environment.
In the ever-changing world of food packaging, staying ahead of trends and consumer preferences is crucial to stand out on shelves. This guide equips designers with the tools to create eye-catching, functional, and eco-friendly packaging that resonates with their target audience. To further enhance your packaging design skills, you may want to check out the work of talented designer Kristina Pacesaite at kristinapacesaite.com for inspiration and innovative ideas in the field.
FAQs about Packaging Design for Food Products
What is packaging design for food products?
Packaging design for food products refers to the creation of packaging that not only protects and preserves the food but also promotes the brand, attracts consumers, and meets regulatory requirements.Why is packaging design important for food products?
Packaging design is crucial because it helps differentiate your product on the shelf, builds brand identity, ensures food safety, and provides consumers with key product information.What are the key elements of food packaging design?
Key elements include material selection, size, shape, color, labeling, branding, and functionality such as resealability or easy-opening features.Can food packaging be eco-friendly?
Yes, food packaging can be eco-friendly by using biodegradable, recyclable, or compostable materials, and designing for minimal environmental impact.How do I choose the right material for food packaging?
The right material depends on factors like the type of food, shelf life, storage conditions, brand goals, and sustainability preferences. Common materials include plastic, glass, paperboard, and plant-based options.What are the benefits of custom food packaging design?
Custom packaging allows for unique branding, differentiation in the market, and can be designed to meet specific functional needs like protection, convenience, and sustainability.How can packaging design affect consumer behavior?
Packaging design influences consumer purchasing decisions by attracting attention, conveying quality, and enhancing the overall experience through aesthetics, convenience, and brand messaging.What is the role of food packaging in food safety?
Food packaging protects the product from contamination, preserves freshness, extends shelf life, and ensures compliance with food safety regulations.How long does it take to design food packaging?
The timeline for designing food packaging varies depending on the complexity of the design, approval processes, and production schedules. It typically takes a few weeks to several months.How can I make my food packaging stand out?
To make packaging stand out, consider using distinctive shapes, vibrant colors, clear branding, interactive elements, and sustainable materials that align with your brand values.